In the last blog we have learned from where the Linux come from and what it is and we also looked at some basic commands like echo, cd, pwd .
In this part we are going to see some more commands and their usage too
Let's deep dive into cd command.
Using cd we can navigate also into backward and forward into directories.
cd directory
I am inside the directory now I can do anything in it like file and directory creation etc.
Now look at some more stuff using cd command.
How can we navigate back to the previous directory from the current directory?
Using cd - command. *
How to get inside the current directory?
cd . : This is the directory we are currently in.
Now suppose in Desktop there is one directory named as newDir and inside it there is one more myDir and we are into the myDir so this is our current directory and how can we go from current directory to previous directory?
Using command cd ..
Creating files and directories
touch: This command is used to create the empty files. we can create multiple files at the same time using this command.
command name: touch
let's create now
I get into the Documents directory and created file there using touch command
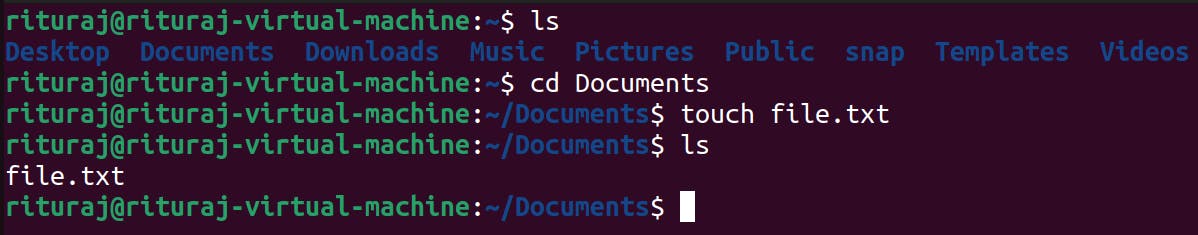
Let's create multiple files in the Documents directory using touch command
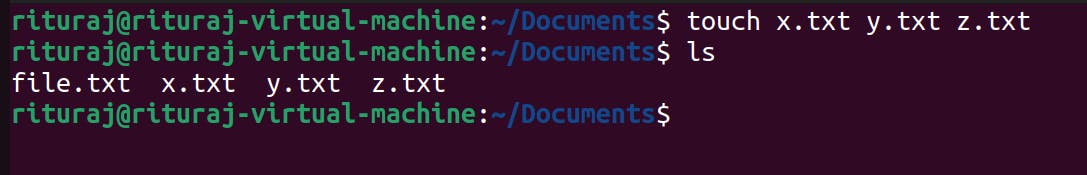
You can create files anywhere in the system by specifying the paths not just by going inside the directory and create it .
but how ? Remember in the previous part we studied about the paths relative path, absolute path. now let's do it first using relative path and then will do using absolute path
So I am going into Documents directory and then from there I will create file.txt file in the Desktop.
cd Documents
touch ~/Desktop/file.txt
ls ~/Desktop : checking from documents only whether the file is created in desktop or not
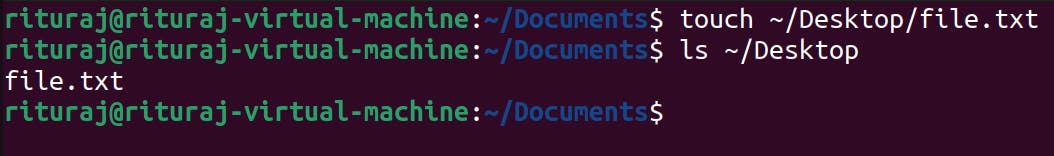
Now let's create using absolute path
touch /home/user/Desktop/file2.txt
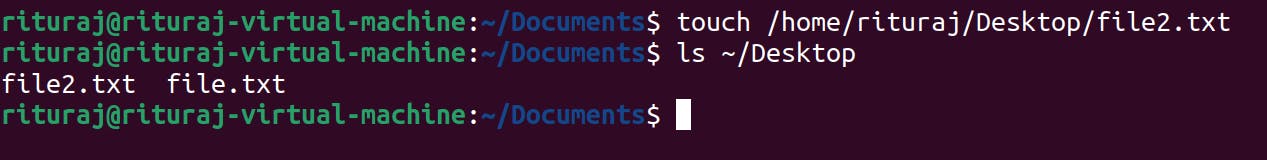
By the way you can create files in Linux without mentioning the extension of the file too. but how?
Its simple using touch command only like
touch myFile
Now see I have not given the extension of the file named as myFile But file is created.
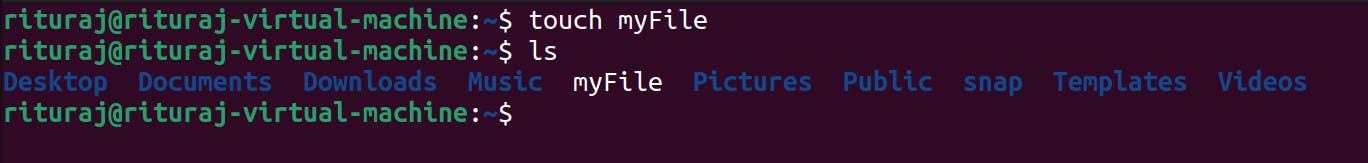
Now what is the reason we without extension of the file we can't say what type of content that file contains but the file is created so how can we check what type of content is there in it.
We can check using file command. This command is used for checking what type of content is there in the file.
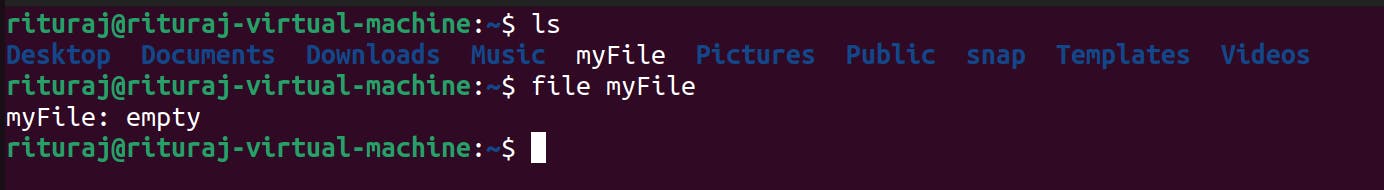
In Linux, filenames aren’t required to represent the contents of the file using file extension. one can create a file called file.gif that isn’t actually a GIF and check exactly what kind of data is there in it.
There are some other ways to create the files also that we will see later
Now see how to create directories
mkdir: This means make directory command and this is used for creating directories (folders).
command name: mkdir
let's create one inside the Desktop
cd Desktop
mkdir myDir: execute ls to check whether directory is created or not.
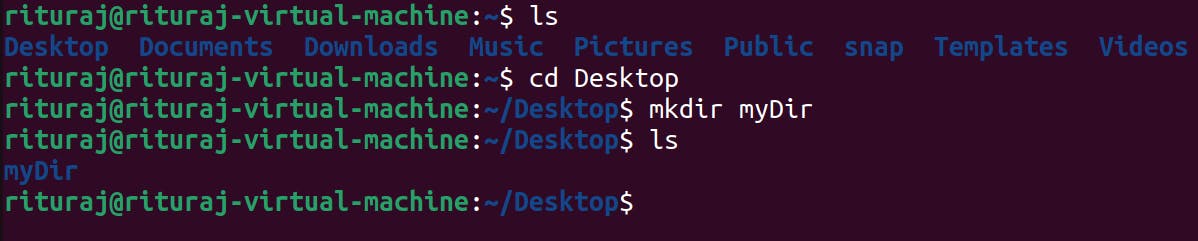
As we have seen above by specifying the paths we can create files from anywhere in the system and the same thing goes with directory too.
let's create
I am in home directory going to create directory in Downloads with going into it.
mkdir ~/Downloads/MyDir
ls ~/Downloads
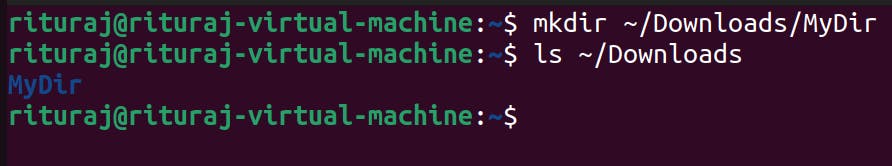
I want you to try creating directories by specifying absolute path. you can any where in the system and try creating directory into other place using absolute path. Do give it a shot.
Let's look at how we can create subdirectories into a directory
mkdir dir1
cd dir1 then inside the dir1 we will do
mkdir sub_dir1
(Try the above commands on your own)
This is simple way to do but there is another way of doing is using mkdir command with flag p.
mkdir -p [parent_dir] / [sub_dir]
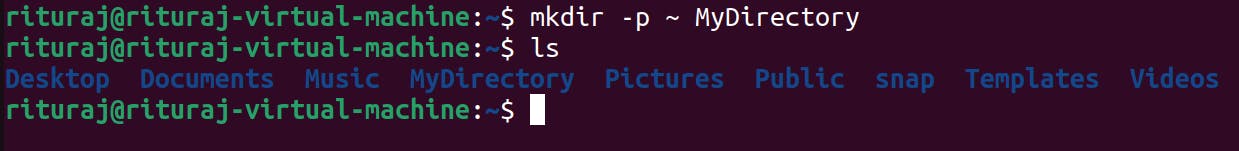
In home directory, I have created a directory named as MyDirectory.
Now we know how to create files and directories in Linux like-systems
In GUI to see the content of the directory we go inside it and then we can see what's there in it.
Similarly in Linux like-systems we use ls command and for going inside the directory we use cd command we study cd command in previous part.
ls: This command is used list out the contents of the directories. By default whenever we apply ls command it will be applied to current directory and will list out the content of the current directory. However while using ls command we can give the path of the directory to list out the content of that.
I am in home directory and let's see what is the content inside it using ls command
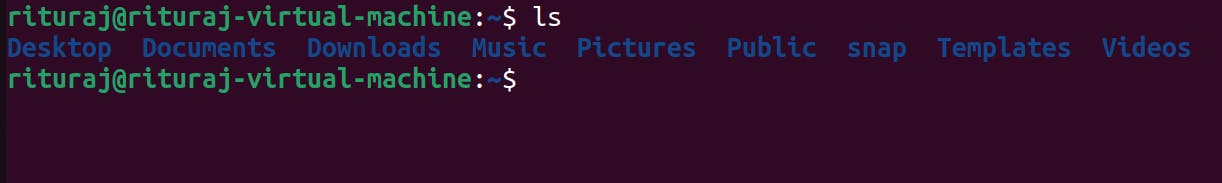
All the content inside the home directory is shown.
What is flags? Flags are the way of setting the options and passing arguments to the commands we run
Now you might wonder what does the flags exactly looks like and how we pass arguments...
you remember above we have used touch command there we are doing
touch file.txt here file.txt is the argument passed to touch command. previously we have cd directory_name here directory name is the argument passed to cd command.
Now look at flags how they look like.
ls -a: It will list out all the content available in the directory including hidden files too.
here -a is the flag.
Lets use ls command with -a flag
ls -a
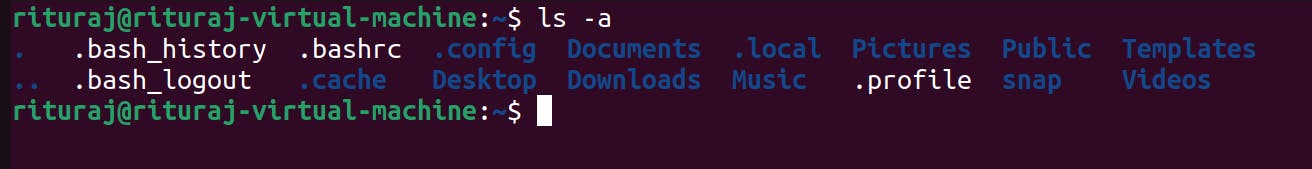
You can see ., ..
In Linux the things start with . (dot) is hidden.**
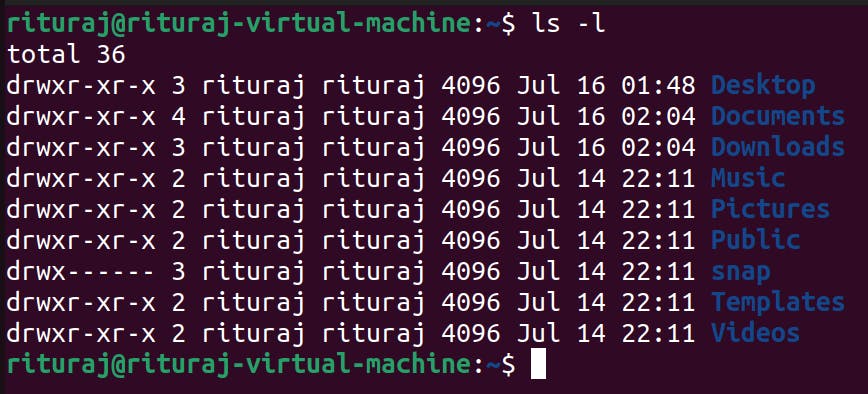
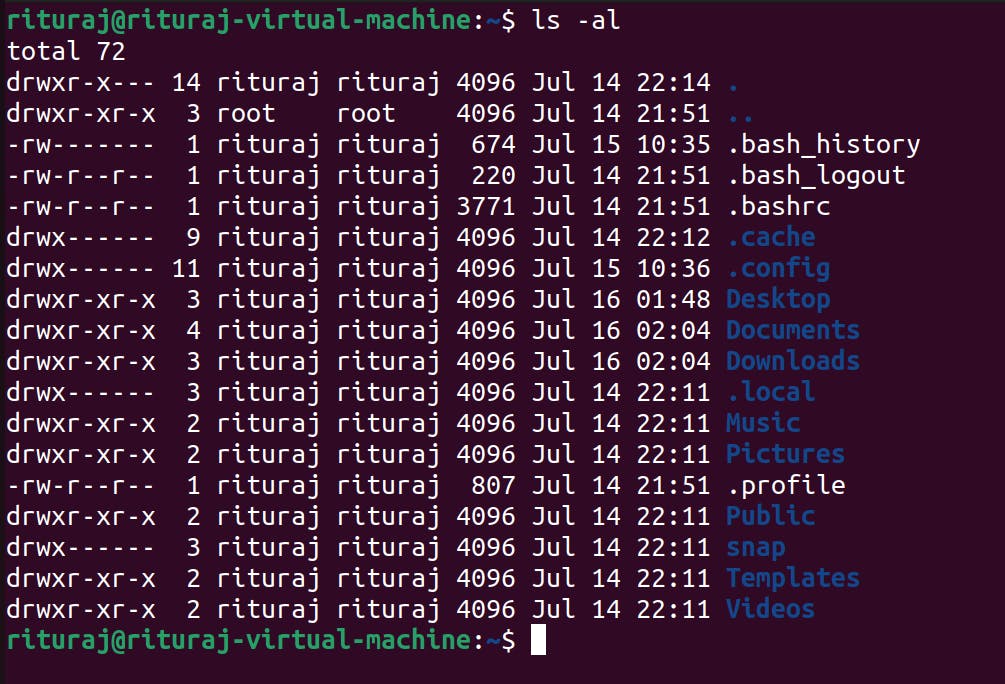
ls -l: It gives a detailed impression of the files and folders present in the directory. It tells about the permission, from which user it is from , size of it, date and time of the last modification.
-l is the flag.
Lets use ls command with -l flag
ls -l
ls -la: → combination of [ls -a] and [ls -l]. It gives a detailed impression of the files and folders present in the directory. It tells about the permission, from which user it is from , size of it, date and time of the last modification including the hidden files and folder too.
here -la is the flag.
ls -al
Lets use ls command with -al flag
We have done lot of stuff now we will learn about some operations that we can do with files and directories.
rm: This command is used to remove the file.
Command name: rm
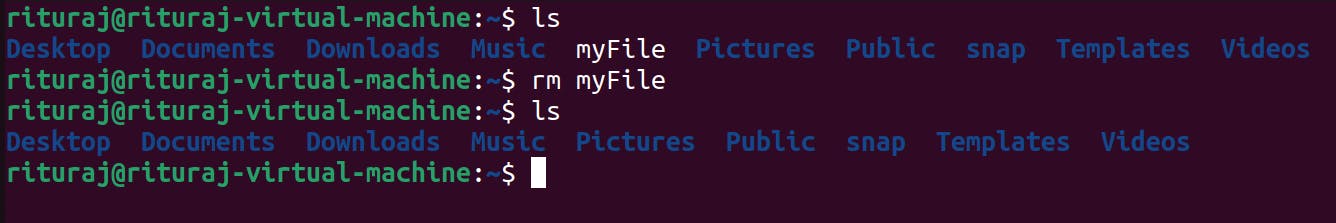
We can remove multiple files also at the same time
let's create and do
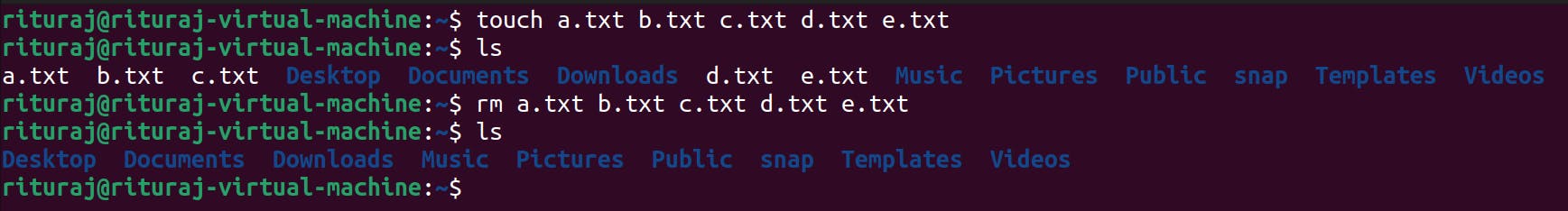
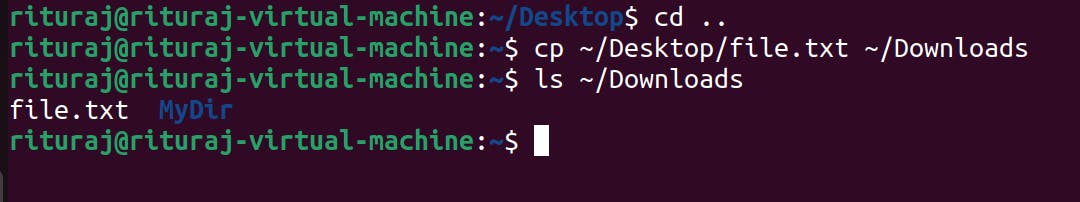
cp: This command is to copy the files from the one location to another.
Command name: cp
cp [file_name] [destination path to copy]
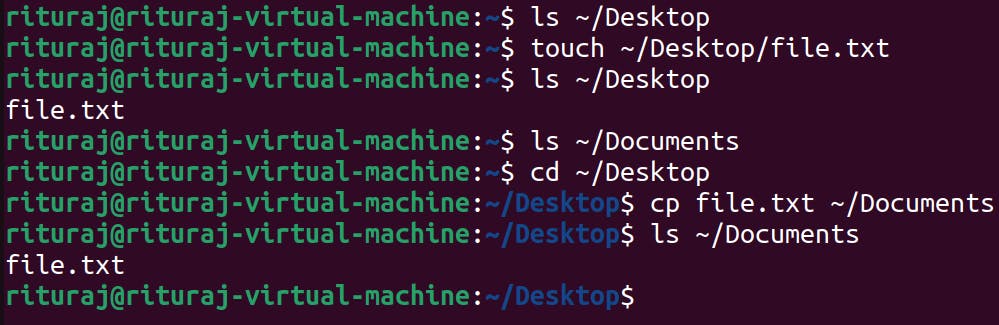
You can also copy the file from source to destination with being present in neither source directory nor destination directory as long as you remember the path.
mv: This command is used to move the files/directories from one location to another.
mv [file_name] [destination path to move]
Command name: mv
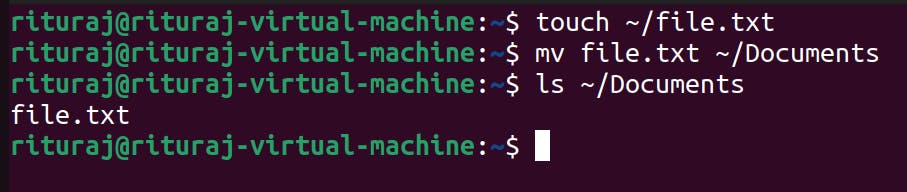
try on your own. You can also move the file from source to destination with being present in neither source directory nor destination directory as long as you remember the path.
mv source_path/folder_inside_the_source/file_name destination path
rmdir: This command is used for removing the directory.
Command name: rmdir
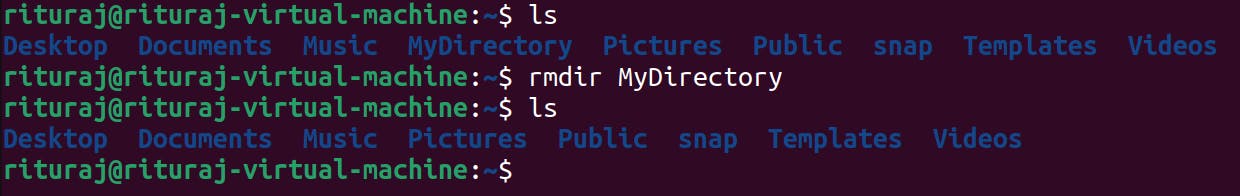
I am removing a directory named as MyDirectory from home directory.
rm -r this means remove recursively.
Suppose there is a dir_x and inside that there is another dir_y then rmdir wont
be able to remove dir_x because it's not empty.
So we have to use rm -r [directory_name]
-r means remove recursively. It will first remove the dir_y inside dir_x and then dir_x.
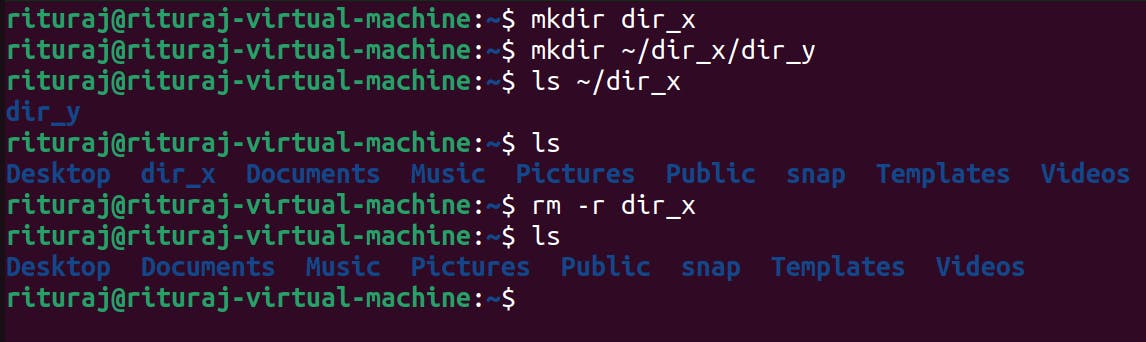
rm -rv [dir_name] : It will delete the directories recursively, directories inside directories and files inside directories will also be removed.
As you can see in the below image that inside a home directory there is one directory myDir and inside it dir1 is there then again inside dir1 there dir2,dir3,dir4 so basically so many directories inside each other.
to all the directories at once we use the command rm -rv [dir_name].
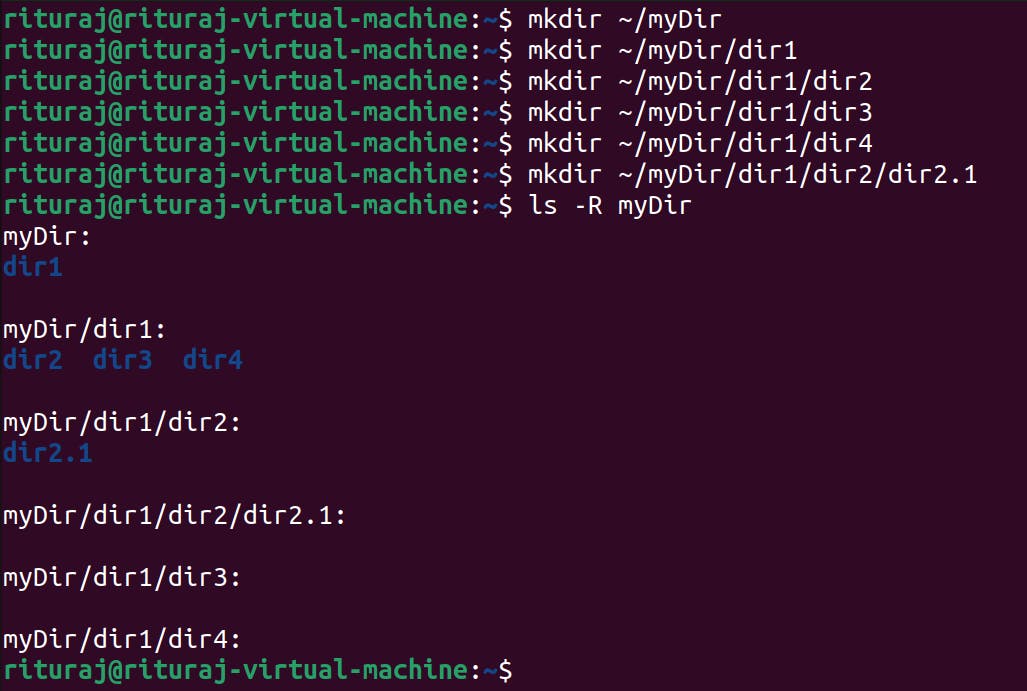
but now you are watching ls -R a new flag which you have seen above then you might be thinking how I got to know about that.
so let's see some helpful commands.
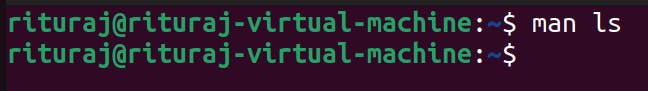
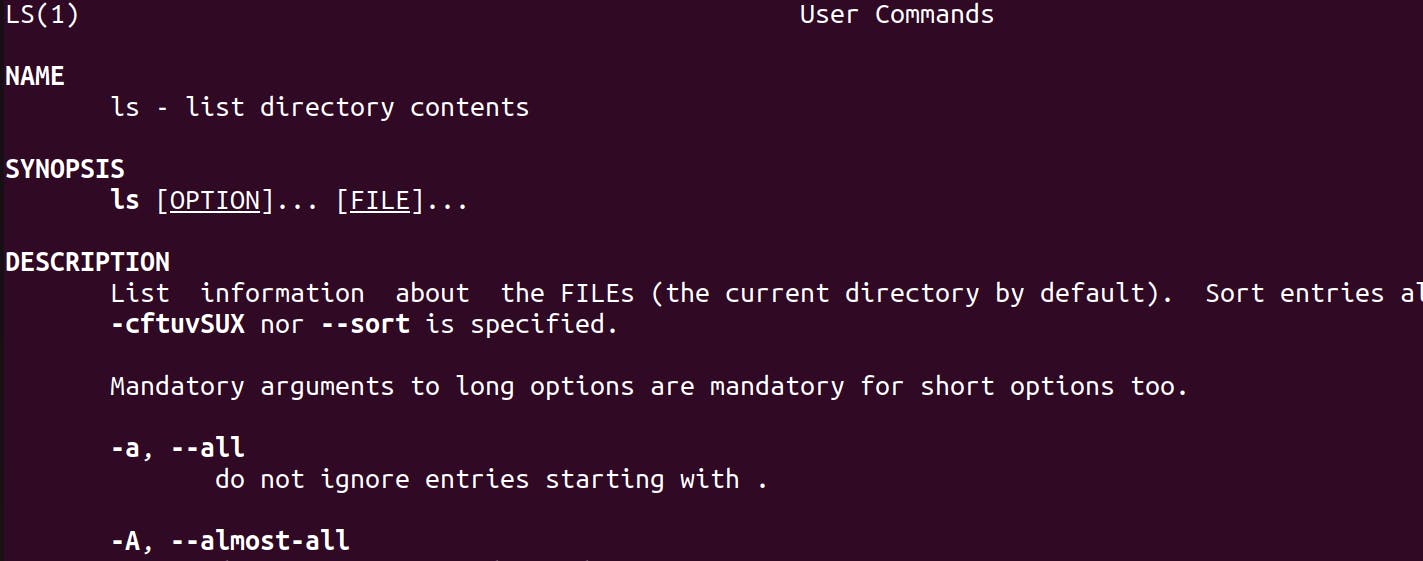
man: It is short for manual. It will show the documentation of any command.
command name: man [command_name]
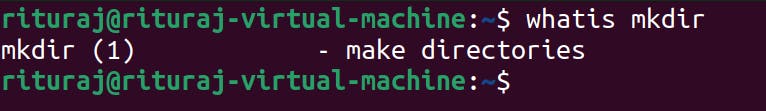
whatis command → It will describe the command in short and will also describe what that command is all about.
I have used to mkdir command you can pass any command as a argument into whatis and check what it is all about.
In the next part we will see some more commands , standard streams and file manipulation.

